Gases are the state of matter with the greatest amount of energy.
Pressure
Pressure is created by gas particles running into the wall of the container. Pressure is measured in many units: 1 atm = 101300 Pa = 101.3 kPa = 760 mm Hg = 14.7 psi. Atmospheric pressure is the pressure due to the layers of atmosphere above us.
Kinetic Molecular Theory
The Kinetic Molecular Theory has several assumptions for ideal gases.
- Gases are made of atoms or molecules
- Gas particles are in rapid, random, constant motion
- The temperature is proportional to the average kinetic energy
- Gas particles are not attracted nor repelled from each other
- All gas particle collisions are perfectly elastic (they leave with the same energy they collided with)
- The volume of gas particles is so small compared to the space between them that the volume of the particle is insignificant
Real gases do have a volume (that takes up space which other particles cannot occupy) and they do have attractions/repulsions from one another as well as in-elastic collisions.
The KMT is used to understand gas behavior. Pressure and volume are inversely proportional. Pressure and temperature are directly proportional. Pressure and number of particles are directly proportional.
An expandable container will expand or contract so that the internal and external pressures are the same. Non-expandable containers will explode or implode if the difference in the pressures is too great for the container to withstand.
Gas Laws
Symbols for all gas Laws:
P = Pressure; V = Volume; n = moles; T = Temperature (in Kelvin);
R = Gas constant 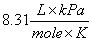 or
or 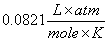
“a” and “b” = correction factors for real gases
Combined Gas Law: 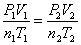 When something is held constant, it cancels out.
When something is held constant, it cancels out.
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure: 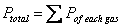
Mole fraction: 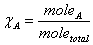 Partial Pressure and mole fraction:
Partial Pressure and mole fraction: 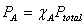
Ideal Gas Law: 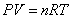 Ideal Gas Law with Molar Mass:
Ideal Gas Law with Molar Mass: 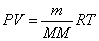
Ideal Gas Law with Density: 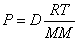
Real Gas Law: 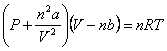
Gas Stoichiometry
Use the molar volume of a gas at STP (1 mole of any gas at STP = 22.4 L) to convert between moles and liters of a gas in stoichiometry. Then use the appropriate gas law to find the volume at non-STP conditions.



