Basic Skills
| Topic Review on "Title": |
Chemistry is an experimental science, therefore it is necessary to be able to work with units and measurements accurately.
Metric System
The metric system is based on prefixes that indicate a power of 10 with base units.
| Metric Prefixes commonly used in chemistry |
Prefix |
Symbol |
Multiple |
Kilo |
k |
1000 |
Deci |
d |
0.1 |
Centi |
c |
0.01 |
Milli |
m |
0.001 |
Micro |
m |
0.000001 |
Nano |
n |
0.000000001 |
SI System
The International System of units gives a standard unit for each type of measurement.
| SI Units commonly used in chemistry |
Measurement |
Unit |
Symbol |
Mass |
Kilogram |
kg |
Volume |
Liter |
L |
Temperature |
Kelvin |
K |
Length |
Meters |
m |
Time |
Seconds |
s |
Amount of substance |
Mole |
Mol |
Energy |
Joule |
J |
Charge |
Coulomb |
C |
There are also some important non-SI units as well.
| Non-SI Units commonly used in chemistry |
Measurement |
Unit |
Symbol |
Length |
Anstrom |
Å |
Pressure |
Atmosphere |
Atm |
Kilopascal |
kPa |
Energy |
Calorie |
cal |
Temperature |
Celcius |
°C |
Taking measurements
Measurements must be taken accurately. Always write down one more decimal place than the instrument tells for certain—a “0” if it’s “one the line” and a “5” if it’s “between the lines.”
Significant Figures
The significant figure rules are to allow people to read data or calculations and know with what precision the data was taken. The significant rules can be summarized in two rules: (1) If a decimal point is not present, count digits starting with the first the first non-zero number and ending with the last non-zero number; (2) If a decimal point is present anywhere in the number, start counting with the first non-zero number and continue until the end of the number. Rules on how to perform calculations with significant figures will be given in a future tutorial.
Fundamental Constants
Several numbers are used throughout chemistry and are important to be familiar with.
Fundamental constants commonly used in chemistry |
Name |
Symbol |
Constant |
Avogadro’s # |
NA |
6.02 X 1023 mol-1 |
Speed of light |
c |
3.0 X 108 m/s |
Gas constant |
R |
8.31 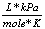 |
0.0821 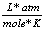 |
Planck’s constant |
h |
6.63 x 10-34 J·s |
Charge of electron |
e |
1.6 x 10-19 C |
Atomic mass unit |
m |
1.66 x 10-24 g |
Std Temp & Pressure |
STP |
273.15 K & 1 atm |
|
| Rapid Study Kit for "Title": |
| Flash Movie |
Flash Game |
Flash Card |
| Core Concept Tutorial |
Problem Solving Drill |
Review Cheat Sheet |
 |
 |
 |
|
| "Title" Tutorial Summary : |
The Metric and SI (International System) of units is used throughout chemistry. The metric system is based on prefixes showing the power of 10 used with base units describing the quantity measured.
Chemistry is an experimental science; therefore it is necessary to take careful measurements. Measurements should always include one more decimal place than the instrument indicates for certain—this last decimal place should be a “0” if the measurement is “on the line” and a “5” if the measurement is “in-between the lines.” Most measurements are understood to be +/- 1 in the last decimal place, unless another uncertainty value is given with the measurement.
Once careful measurements are taken, the precision with which they were measured can not be heightened while doing calculations, nor should it be lost and allowed to become less precise. Therefore, there are rules about counting “significant figures” which indicate which were measured for certain. Rules on performing calculations with significant figures will be introduced in a later tutorial.
There are many other “Basic skills” needed in chemistry, but they will be introduced throughout the tutorial series when they are needed.
|
| Tutorial Features: |
Series Features:
- Concept map showing inter-connections of new concepts in this tutorial and those previously introduced.
- Definition slides introduce terms as they are needed.
- Visual representation of concepts
- Animated examples—worked out step by step
- A concise summary is given at the conclusion of the tutorial.
|
| "Title" Topic List: |
- The Metric and SI Systems
- Metric prefixes
- SI units
- Common non-SI units
- Measurement and Uncertainty
- Tools common in Chemistry Labs
- Taking measurements
- Uncertainty
- Significant Figures
- Why they’re used
- How to count them
- Fundamental Constants used in Chemistry
- Brief overview of topics to be included in future tutorials:
- The language of chemistry
- The periodic table
- Dimensional analysis
- Scientific notation
- Use of scientific calculators
|
See all 24 lessons in college chemistry, including concept tutorials, problem drills and cheat sheets:
Teach Yourself College Chemistry Visually in 24 Hours |



